Diabetic Retinopathy
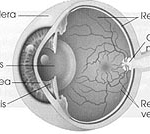
WHAT IS RETINA?
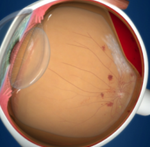
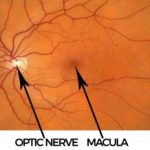
Retina is inner layer of the eye where images are formed and transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain that how one can see. Retina has mainly four parts
- General retina
- Optic Nerve
- Macular
- Blood Vessels
In the present era, diabetes has become one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness. Anyone with Diabetes is at risk of developing Diabetic Retinopathy, without early detection and treatment diabetic retinopathy can permanently damage the retina.
There are two types of Diabetic Retinopathy that are sight threatening:
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
- Diabetic Maculopathy (DM)
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
In PDR vision can be completely normal. Some patients go to opticians /family physician/ Diabetiologist and sometimes they check vision and inform patient that all is good which is not true.The only way to diagnose PDR is to dilate the pupil and through examination by ophthalmologist
WHAT IS PDR?
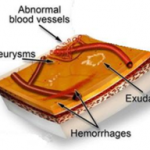
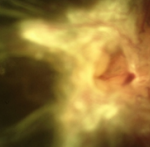
Due to the reduced blood circulation in the retina, new blood vessels form on the surface of the retina and optic disc. Unfortunately these new vessels are weak and can bleed. Subsequently, at a later stage, this leads to formation of scar tissue on the retina. This scar tissue pulls and distorts theretina. This is what causes a retinal detachment.
TREATMENT OF PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY.
The most sight threatening diabetic problems can be prevented by laser treatment if it is detected early enough. It is important to realize however that laser treatment aims to save the sight you have – not make it better. The modern method of management here is to perform PAN retinal Argon Laser photocoagulation.

PAN retinal photocoagulation
Dr. Joshi performing laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy.
Laser Eye Centre (Dr. Joshi) is the first centre in East Africa offering such treatment since 1990.
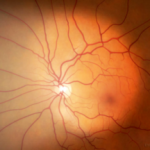
Showing resolution of hemorrhage and neovascularization following laser pan-retinal photocoagulation
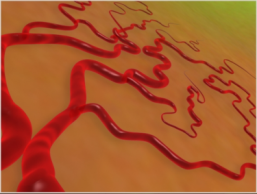
Neovascularization and hemorrhage of blood vessels
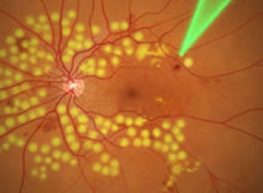
Pan-retinal Laser photocoagulation

Resolution of hemorrhage; blood vessels shrink after treatment
It is very important to control the blood pressure and lipid profile. Laser stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Laser light is low energy, coherent light of a wavelength whose energy is non – divergent and works together in one direction. It can thus be focused to a tiny spot, and be used surgically to treat eye problems. Lasers work with radiation generated from light with many tiny energy pulses. Laser light can be controlled so precisely, it is safe and reliable. The Principle: as mentioned earlier, in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy, the retina is not getting enough oxygen thus new blood vessels form.
The principle of PAN retinal photocoagulation is that with light laser marks the laser is done avoiding the central, important area (macula), [check the anatomy of the eye] which is for focusing and colour vision, whilst in the remaining peripheral part laser is done so that oxygen requirement of the retina is reduced and whatever oxygen is available goes to the central important part.
Patient with Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy can have perfectly normal vision; thus vision is not the criteria for diagnosis or suspected Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. The only way to find out is by dilating the pupil, for examination by an ophthalmologist. If it is detected at an early stage the PAN retinal photocoagulation works in 90% of the patients otherwise untreated Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy leads to blindness.
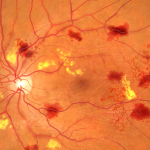
UNTREATED DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
End stage: Traction bends leading to detachment of the retina
Patients who have been diabetic for 5 years have a 25% chance of developing Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy while at 10 years they have a 50% chance and at 20 years they would have a 98% chance of developing this condition
DIABETIC MACULOPATHY (DM) AND LASER TREATMENT
RETINA
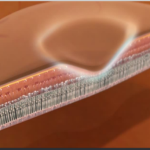
CROSS-SECTION OF MACULA
At the centre of the retina is the macula which is a small area about the size of a pinhead. This is the most highly specialized part of the retina and it is vital because it enables you to see fine detail and read small print.
DIAGNOSES OF DIABETICMACULOPATHY(DME)
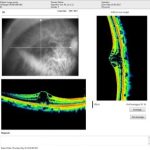
Apart from clinical examination of retina and macula, the latest break through in early diagnoses is achieved by OCT.
In diabetic Maculopathy, the macula becomes swollen due to leakage from the retinal blood small blood vessels. Laser is applied to the leaking spots, sealing and preventing further deterioration of central vision and hence stabilizing it.
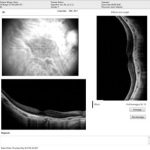
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY TEST (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a test which gives the cross-section of the retina which is clinically not visualized.
With the latest technological innovations and advances in OCT, it has become an invaluable diagnostic tool for DME as it allows an objective evaluation with effectiveness in both qualitative and quantitative description of the pathology and hence gas becomes a standard tool in the management of DME. Its use allows more precise evaluation of retinal pathology in DME and precise Retinal thickness and edema

OCT TEST: SHOWS THE FUNCTION OF THE RETINA
OCT Showing Diabetic Macula Edema
TREATMENT OF DME (Diabetic Macula Edema)
Treatment of DME is a collaborative effort and treatments cannot cure DME but will slow down the progression of vision loss.
DME is a chronic condition and monitoring and follow up remains an essential part of treatment.
1. AntiVEGF therapy:
anti vascular endothelia growth factor drugs (ranibizumab- *Lucentis –the most effective) are injected into your eye to help prevent the vascular endothelial growth factor from triggering abnormal leakage of blood vessels into the macula. This is the most effective treatment for DME.
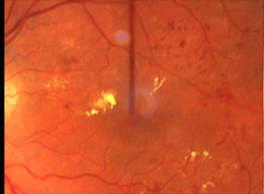
Before laser treatment
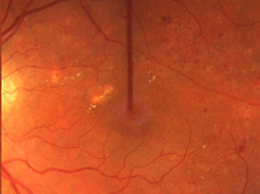
After laser treatment
3. Injectable slow release corticosteroid –
an injectable implant is placed at the back of the eye slowly releasing corticosteroids for upto 3 years which helps in reducing the inflammation associated with DME
DIABETES AND CATARACT:
Diabetic patients are 5times more prone to develop cataracts. The only way to treat cataracts is by extraction. Cataract extraction by Phacoemulsification is the best way to remove a cataract in diabetic patients. In this new method of cataract surgery the incision is very small, and is (normally) self-sealing and does not require any stitches, thus there is no suture tension discomfort. Patients have improved vision after 2-3 days. Patients can resume their daily physical activities almost immediately.
This favour diabetic patient as there is less trauma to the eye so Postoperative inflammation is minimal and astigmatism or distortion of the cornea is reduced.
Further advances in Cataract surgery known as the Micro Incision Phaco means the size of the incision is reduced a further 25% from 3.2mm to 2.4 mm.